Use of the Viscometer for Painting Processing

Consistent good processability takes precedence over the obvious requirement of an almost identical coating material composition, which can be very complex. Even if the composition can be assumed to be identical, such a batch may differ fundamentally from the previous delivery during processing or with respect to stability. However, the quality of the coating (also in this case representative of all coating materials) – as well as that of the coating that is subsequently finished – consists in its usefulness or suitability to the needs of the customer, and that:
The Viscometer in the Textile Sector

Viscosity is an important parameter in the textile industry. For example, in the production of rayon, particularly before and during the spinning phase of rayon fibers. The fibers of this material are made of pure cellulose and for its elaboration, cellulose is transformed into continuous filaments, in a process that must be controlled.
What are the types of Viscometer?

A viscometer is a device used to measure the viscosity of liquids and their flow properties. These equipments have different applications in different types of substances and materials, such as oil, plastic, paints, coatings, adhesives, wax and asphalt. It is also used in the food and beverage industry and in the manufacture of personal toiletries.
The Viscometer for the manufacture of Medicines

The pharmaceutical industry faces many challenges, as it must produce drugs with the highest quality standards at prices that are accessible to the population seeking to heal some ailment. In this sense, it is necessary to sustain intermediate and final quality parameters in the production process of drug manufacture, constantly making appropriate measurements.
Preventive Maintenance of the Viscometer

Preventive maintenance is what we do to the equipment, on a regular and routine basis in order to ensure its operation and avoid periods of inactivity due to unexpected failures of the device. For the maintenance strategy to be successful, we must plan and deliver on a program. This includes the recording of records on the activities carried out, linked to maintenance.
Thermal cycler: How do you work?

A thermal cycler or also called thermal sequencer is a laboratory equipment that allows to carry out the amplification of DNA molecules by means of the PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique, through cyclical changes in temperatures that generate at their once strand amplification of this nucleic acid. This equipment is used for qualitative amplifications or even to quantify the amount of amplified DNA.
What is a thermal cycler?

The thermal cycler is a device that allows the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) efficiently and quickly; by means of the automatic and cyclical realization of the temperature changes that are required for the amplification of a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) chain; from a thermostable enzyme.
Importance of the Patient Monitor for the early identification of complications in patients
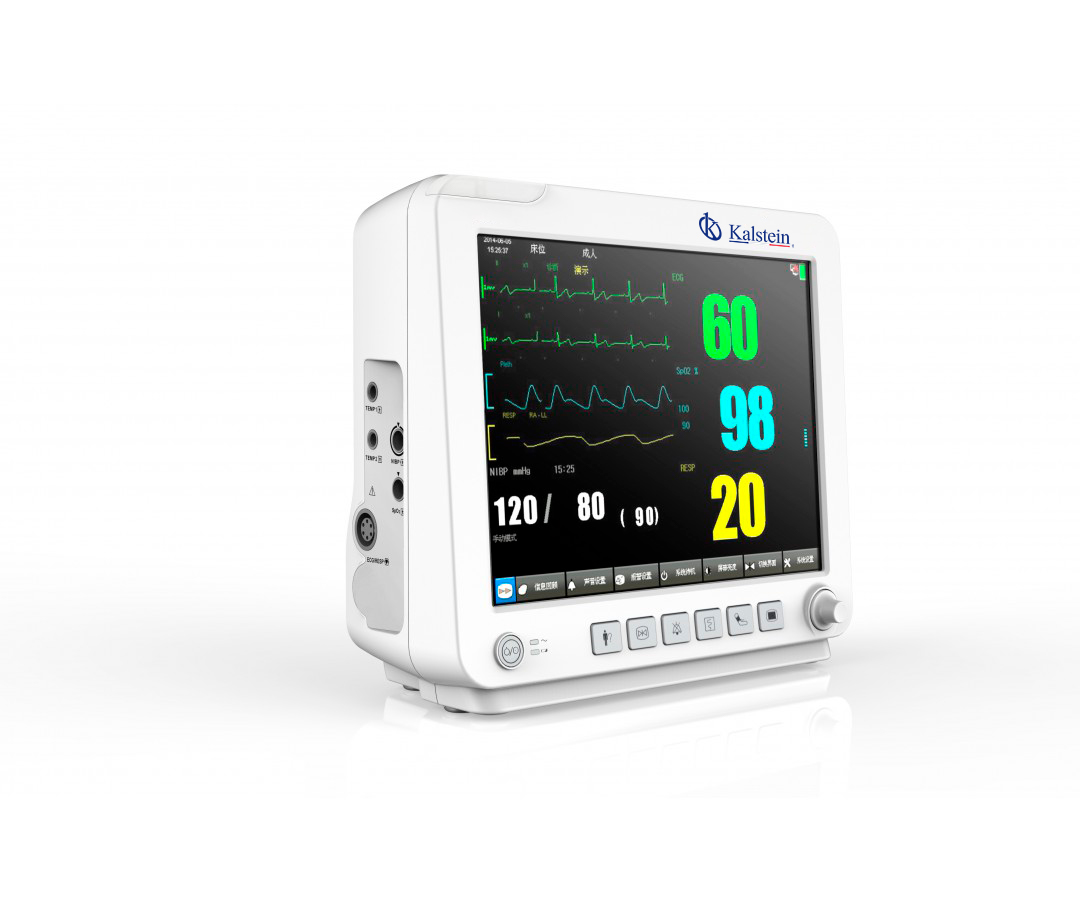
The patient monitor is an increasingly popular tool in the medical field for the early identification of complications in patients. This tool provides continuous monitoring of the most important clinical parameters, such as blood pressure, body temperature, heart rate, and oxygen saturation index, to detect any significant changes in time. Through this continuous monitoring of the main vital indicators, warning signs can be established to act early and prevent complications that can put people’s lives at risk.
PCR thermocycler: characteristics and uses

A thermocycler is a laboratory equipment also called a thermal sequencer. This equipment allows to obtain the amplification of DNA molecules by PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) technique, through cyclical changes of temperatures that generate in turn the amplification of strands of this nucleic acid.
Storage of vaccines with the use of lyophilizers
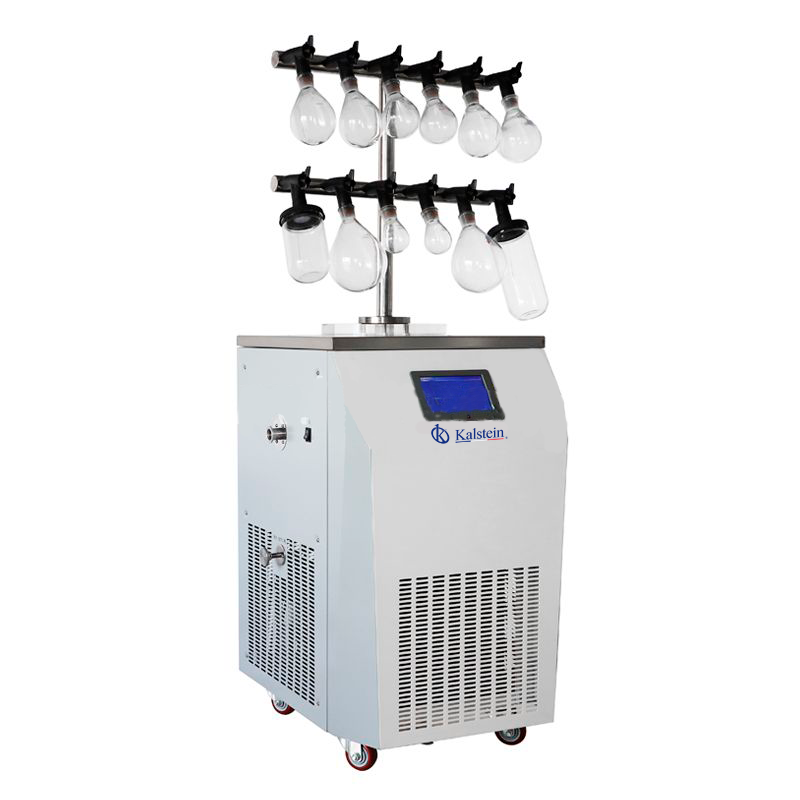

It is a process of stabilization of a product, in which it is dried under vacuum by freezing it and removing the water present by sublimation and desorption, in such a way that there is no change in its basic structure or in its chemical composition, and the likelihood of reaction between its components and microbiological growth is minimized. This procedure is also called Freeze-drying and the finished product is characterized by being a solid, fragile network with high porosity, and soluble in water.
